Country: Armenia
Further insights from Armenia, Guatemala, Malaysia, Niger, and Tunisia illustrate access to information challenges
December 10, 2024 – New research from Transparency International Defence & Security (TI-DS) underscores the need for better access to information in the defence sector to curb corruption, ensure accountability, and improve civic engagement.
Published today, Unlocking Access: Balancing National Security and Transparency in Defence shines a light on opaque defence sectors worldwide at a time of increased geopolitical tensions and global military spending reaching record highs of $2.4 trillion.
The report highlights challenges and good practices of transparency in defence budgets, procurement and policy processes using detailed case studies from Armenia, Guatemala, Malaysia, Niger, and Tunisia. The countries are at varying stages of progress in advancing access to information in their defence sectors and face a range of challenges, including conflict-driven secrecy, democratic backsliding, and stalled reforms.
Our analysis reveals that while international frameworks provide guidelines for transparency, implementation remains weak. Blanket national security exemptions are often used to justify withholding critical information, while public interest tests designed to balance the benefits of disclosing against the potential harm are mostly absent.
This lack of transparency increases the risk of corruption, mismanagement of funds, and fuels public distrust of the very institutions tasked with protecting citizens.
Michael Ofori-Mensah, Head of Research at Transparency International Defence & Security, said:
“The defence sector remains one of the most secretive corners of government, making it a breeding ground for corruption. Striking a balance between national security and the public’s right to know is crucial to ensure accountability, but far too often governments tip the scales towards secrecy. It’s time for transparency to be the rule, not the exception.”
Case study insights
Armenia has kept high levels of defence spending because of its decades-long conflict with Azerbaijan over the Nagorno-Karabakh territory, which recently concluded with major losses for Armenia. Access to information was enshrined in a 2003 national freedom of information law but has been severely curtailed by the 2024 states secrets law, which prohibits the release of information related to most defence spending.
Guatemala has endured a growing corruption crisis for the past decade, as the presidency and the powerful Public Prosecutor’s office stifled anti-corruption efforts, forced anti-corruption officials into exile, and blocked potential reform candidates from elections. As the Secretariat for Access to Public Information is required to work with the Prosecutor’s Office on access to information enforcement, implementation of the law has faltered until now.
Malaysia saw a peaceful power transition in 2018, but governance reforms – including access to information – have stalled, with the Official Secrets Act 1972 (OSA) severely limiting access to information. The OSA functions as the de facto national framework for access to information and overrules any other legislation on information access. There is little knowledge about the defence budget or expenditures, and almost no publicly available information about acquisition planning.
Niger experienced a military coup in July 2023 that has led to increased violence, stark reductions in foreign assistance, and a severe curtailing of access to information and other democratic rights. Even prior to the coup, defence income and military spending were mainly non-transparent, as were defence purchases. But a new far-reaching law was passed in 2024 that excludes all defence matters from public procurement, public accounting, and taxes.
Tunisia has seen democratic backsliding since 2021 which reduced government transparency. Though a strong access to information law exists, defence-related information is often kept confidential. Still, Tunisia has a strong access to information law, with an effective independent oversight body that has helped to implement the law throughout the public sector.
The report offers specific recommendations for each of these five countries to improve access information which broadly fit into these categories:
- Balancing tests: Legal frameworks should require officials to assess the public interest versus potential harm before withholding information.
- Proactive disclosure: Governments should regularly and proactively publish defence budgets, procurement plans, and financial results to enhance accountability.
- Independent oversight: Review bodies should be established to monitor and adjudicate disputes over information access.
- Civil society engagement: Defence planning and policymaking should be open to civil society for broader input and oversight
Notes to editors:
The case studies in Unlocking Access were produced using an updated version of our Government Defence Integrity Index 2020 – the leading global assessment of the governance of and corruption risks in defence sectors. The data was supplemented by interviews with local experts, and the review of policy reports and media investigations.
French and Spanish versions of this press release are available.
Despite widely agreed international standards for access to information in the defence and security sector, transparency remains insufficient to ensure accountability. National security exemptions are frequently applied in vague and undefined ways, limiting the release of precise, timely and detailed information that is crucial for understanding how government is functioning and protecting public interest, especially in areas as fundamental as national security.
Read the launch press release:
Information exchange within government facilitates various types of accountability – from parliamentary scrutiny of executive decisions, to audits of the government’s use of public funds as well as disciplinary sanctions for public officials. More importantly, information disclosure to the public by government bodies also forms the foundation for meaningful citizen engagement and accountability. This is true not just for voting and activism, but for interest in the policies that determine the course of daily life, including whether the security forces are absent, overmilitarised, or well-balanced.
Legitimate national security interests are best safeguarded when the public is well-informed about government activities, including those undertaken to ensure safety and protection. Access to information enables public scrutiny of government action and facilitates public contribution to policymaking and national debate, thus serving as a crucial component of genuine national security, democratic participation, and sound policy formulation. Access to information is also a specific aspect of governance that involves the intentional disclosure of information. These policies require the release of information that is relevant to the public, and is also accessible, accurate and timely.
This report provides an overview of the state of defence transparency and access to information related to defence and security sectors worldwide, drawing on the Government Defence Integrity (GDI) database on institutional integrity and corruption risk. In light
of increasing global military spending (with a new world record of $2.443 trillion recorded in 2023) the overarching focus is on access to defence-related financial information, as transparency and appropriate oversight of defence finances remain critical for public
accountability, among others.
Further, this report also includes a review of global standards for transparency that apply to the defence sector, specifically the UN Convention Against Corruption (UNCAC) and the Global Principles on National Security and the Right to Information (or Tshwane Principles). This is coupled with specific exploration of five country cases (Armenia, Guatemala, Malaysia, Niger, and Tunisia) and insights from their legal frameworks and implementation experiences. It concludes with recommendations for good practice to enhance access to information.
|
|
|
Access to information is a cornerstone of healthy, accountable and transparent societies and essential for democracy.
By improving the public’s ability to obtain and use government-held information, citizens are empowered to participate fully in democratic processes, make informed decisions, and hold their leaders accountable.
Access to information is vital in all public sectors, but particularly so in defence and security where high levels of secrecy combined with substantial public budgets greatly increase the risk of corruption. Transparency and access to information in this sector provides a crucial bulwark against the misuse of funds, ensures accountability, and maintains public trust.
Ahead of Access to Information Day 2024, we’re excited to share details of our upcoming report which provides a comprehensive overview of the state of defence transparency and access to information worldwide.
Our report aims to strengthen accountability by enhancing access to defence information, in line with our broader goal to ensure informed and active citizens drive integrity in defence and security.
Utilising our Government Defence Integrity (GDI) 2020 database, which assesses institutional integrity and corruption risks, the report offers a detailed assessment of global defence transparency and access to information, with a focus on defence finances including budgeting information and spending practices. This is particularly urgent in an era of increasing military spending. The latest defence spending data from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) shows world military expenditure rose for the ninth consecutive year to an all-time high of $2.443 trillion in 2023. This represents an increase of 6.8 per cent in real terms from 2022, which is the steepest year-on-year increase since 2009.
Additionally, the report also includes a review of global standards for transparency that apply to the defence sector. This is coupled with insightful case studies from Niger, Tunisia, Malaysia, Armenia and Guatemala and a review of good practices. The report concludes with recommendations to enhance access to information in particular contexts.
We look forward to sharing the full report and the accompanying case studies shortly. Updates on the launch date will be provided via our X/Twitter and LinkedIn accounts.
New research from Transparency International Defence & Security warns of high corruption risk across CEE region
December 9 – Decades of progress towards greater democratisation across Central and Eastern Europe (CEE) threatens to be undone unless urgent steps are taken to safeguard against corruption, new research from Transparency International warns.
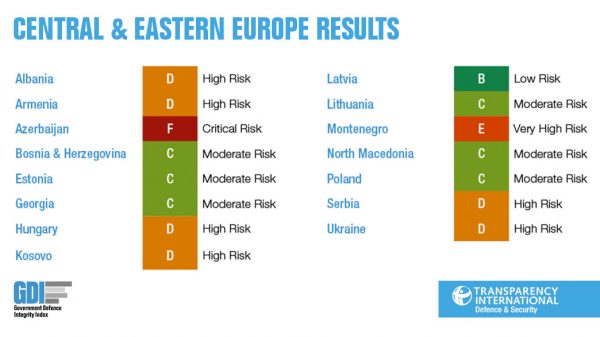
The Government Defence Integrity Index (GDI) finds more than half of the 15 countries assessed in the region face a high risk of corruption in their defence and security sectors.
Released today, Progress [Un]Made identifies region-wide issues which provide fertile ground for corruption and the deterioration of governance. These include weak parliamentary oversight of defence institutions, secretive procurement processes that hide spending from scrutiny, and concerted efforts to reduce transparency and access to information.
These issues are compounded by the huge amounts of money involved, with spiralling military expenditure in the CEE region topping US$104 billion in 2019 as many states continue to modernise their defence and security forces. The 15 states featured in the report are responsible for a quarter of this total with the majority increasing their defence budgets in the last decade.
Natalie Hogg, Director of Transparency International – Defence & Security, said:
“Following major strides towards more robust defence governance in Central and Eastern Europe, many of these results should be a cause for concern. Corruption and weak governance in the defence and security sector is dangerous, divisive and wasteful. While it is encouraging to see a handful of countries score well the overall picture for the region is one of high corruption risk, especially around defence procurement – an area responsible for huge swathes of public spending.”
The GDI provides a detailed assessment of the corruption risks in national defence institutions by scoring each country out of 100 across five key risk areas: financial, operational, personnel, political, and procurement. Highlights from the CEE results include:
- Average score for the region is 48/100, indicating a high risk of corruption.
- Montenegro is judged to be at ‘very high’ risk with a score of 32, while Azerbaijan’s score of just 15 places it in the ‘critical’ risk category.
- High levels of transparency see Latvia fare the best in the region, with a score of 67 indicating a low risk of corruption.
- Authoritarian governments have weakened parliamentary oversight (Poland) and restricted access to information regimes (Hungary), closing off a key sector off from public debate and oversight.
We identify five key themes that are increasing corruption risk across the region, including:
Weak parliamentary oversight
Parliamentary oversight of defence is a key pillar in enforcing transparency and accountability but only two of the 15 countries we assessed have retained truly robust parliamentary oversight.
CEE regional average score: 51/100 (Moderate risk)
Best performers: 1) Latvia: 94/100 (Very low risk); 2) Lithuania: 83/100 (Very low risk)
Worst performers: 1) Azerbaijan 12/100 (Critical risk); 2) Hungary 27/100 (Very high risk)
Opaque procurement processes
Allowing companies to bid for defence contracts helps reduce the opportunities for corruption and ensure best value for taxpayers, but our analysis highlights that open competition in this area is still the exception rather than the norm.
CEE regional average score: 47/100 (High risk)
Best performers: 1) North Macedonia 82/100 (Low risk); 2) Estonia: 74/100 (Low risk)
Worst performers: 1) Azerbaijan 8/100 (Critical risk); 2) Hungary 14/100 (Critical risk)
Attacks on access to information regimes
Access to information is one of the basic principles of good governance, but national security exemptions and over-classification shield large parts of the defence sector from public view.
CEE regional average score: 55/100 (Moderate risk)
Best performers: 1) Georgia, Latvia, North Macedonia, Poland 88/100 (Very low risk); 2) Lithuania: 75/100 (low risk)
Worst performers: 1) Azerbaijan 13/100 (Critical risk); 2) Hungary 25/100 (Very high risk)
To make real progress and strengthen the governance of the defence sector in the region, Transparency International calls on governments across the region to:
- Respect the independence of parliaments and audit institutions and provide them with the information and time they need to perform their crucial oversight role.
- Overhaul their procurement systems to ensure more competition and transparency.
- Guarantee transparent and effective access to information and implement a clear rationale on the use of the national security exception, as well as transparency over how the rationale is applied.
Notes to editors:
Progress [Un]Made – Defence Governance in Central and Eastern Europe can be downloaded here.
The CEE region spent US$104 billion on defence and security in 2019. This total includes Russia, which spent US$65 billion. Lithuania and Latvia increased military spending by 232 per cent and 176 per cent respectively between 2010 and 2019, and Poland by 51 per cent over the same period. Armenia and Azerbaijan consistently spend close to 4% of GDP on defence and are among the most militarised countries in the world.
Whilst defence governance standards in Europe are some of the most robust globally, states in Central and Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, where a combination rising defence budgets and challenges to democratic institutions, are particularly vulnerable to setbacks to their recent progress in governance and development.
In Armenia, Albania, Hungary, Kosovo, Montenegro, Poland and Serbia, there is a notable tendency for parliaments to align themselves with the executive on defence matters, for example by passing executive-sponsored legislation with no or only minor amendments.
In Georgia, secret procurement accounted for 51 per cent of total procurement procedures from 2015-2017. In Ukraine that figure is 45 per cent, while in Poland it is as high as 70 per cent. In Lithuania, open competition accounted for as little as 0.5 per cent of procurement procedures, with upwards of 93 per cent of defence procurement conducted through restricted tenders and negotiated procedures.
In Hungary, the government has made it harder to access information by skewing the rules in favour of public bodies and imposing new fees on those who lodge requests. In Estonia, the 2013 access to information act contained 7 exceptions, with 1 related to defence; by 2018, there were 26 exceptions, with 7 related to defence. Just three of the 15 states we assessed – Lithuania, Latvia and Georgia – were found to have been responding to freedom of requests promptly and mostly in full.
About Transparency International
Through chapters in more than 100 countries, Transparency International has been leading the fight against corruption for the last 27 years.
About the Government Defence Integrity Index
The GDI is the only global assessment of the governance of and corruption risks in defence sectors, based upon 212 indicators in five risk categories: political, financial, personnel, operations and procurement.
The Central and Eastern Europe wave includes assessments for 15 countries: Poland, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Ukraine, Armenia, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Serbia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Kosovo, Albania, Montenegro and North Macedonia. All states are either EU/NATO members or accession/partner states.
The GDI was previously known as the Government Defence Anti-Corruption Index (GI). The Index underwent a major update for the 2020 version, including changes to the methodology and scoring underpinning the project. This means overall country scores from this 2020 version cannot be accurately compared with country scores from previous iterations of the Index.
Subsequent GDI results will be released in 2021, covering Latin America, G-20 countries, the Asia Pacific region, East and Southern Africa, and NATO+.
Contact:
Harvey Gavin
harvey.gavin@transparency.org.uk
+44 (0)20 3096 7695
+44 (0)79 6456 0340 (out of hours)
This report examines the quality and effectiveness of defence governance across fifteen countries in Central and Eastern Europe: Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Estonia, Georgia, Hungary, Kosovo, Latvia, Lithuania, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Poland, Serbia and Ukraine. It analyses vulnerabilities to corruption risk and the strength of institutional safeguards against corruption across national defence sectors, drawing on data collected as part of Transparency International Defence & Security’s (TI-DS) Government Defence Integrity Index (GDI).
It is intended to provide governments and policymakers with an analysis of defence governance standards in the region and supply civil society with an evidence base that will facilitate their engagement with defence establishments and support advocacy for reforms that will enhance the transparency, effectiveness and accountability of these institutions.
This report details good practice guidelines and policy implications that are designed to reduce the opportunities for corruption and improve the quality of defence governance in Central and Eastern Europe. It identifies five key issues of defence governance where improvements are urgently needed in order to mitigate corruption risks: parliamentary oversight, defence procurement, transparency and access to information, whistleblowing, and military operations.

