Theme: Procurement
By Ara Marcen Naval, Head of Advocacy – Transparency International Defence & Security
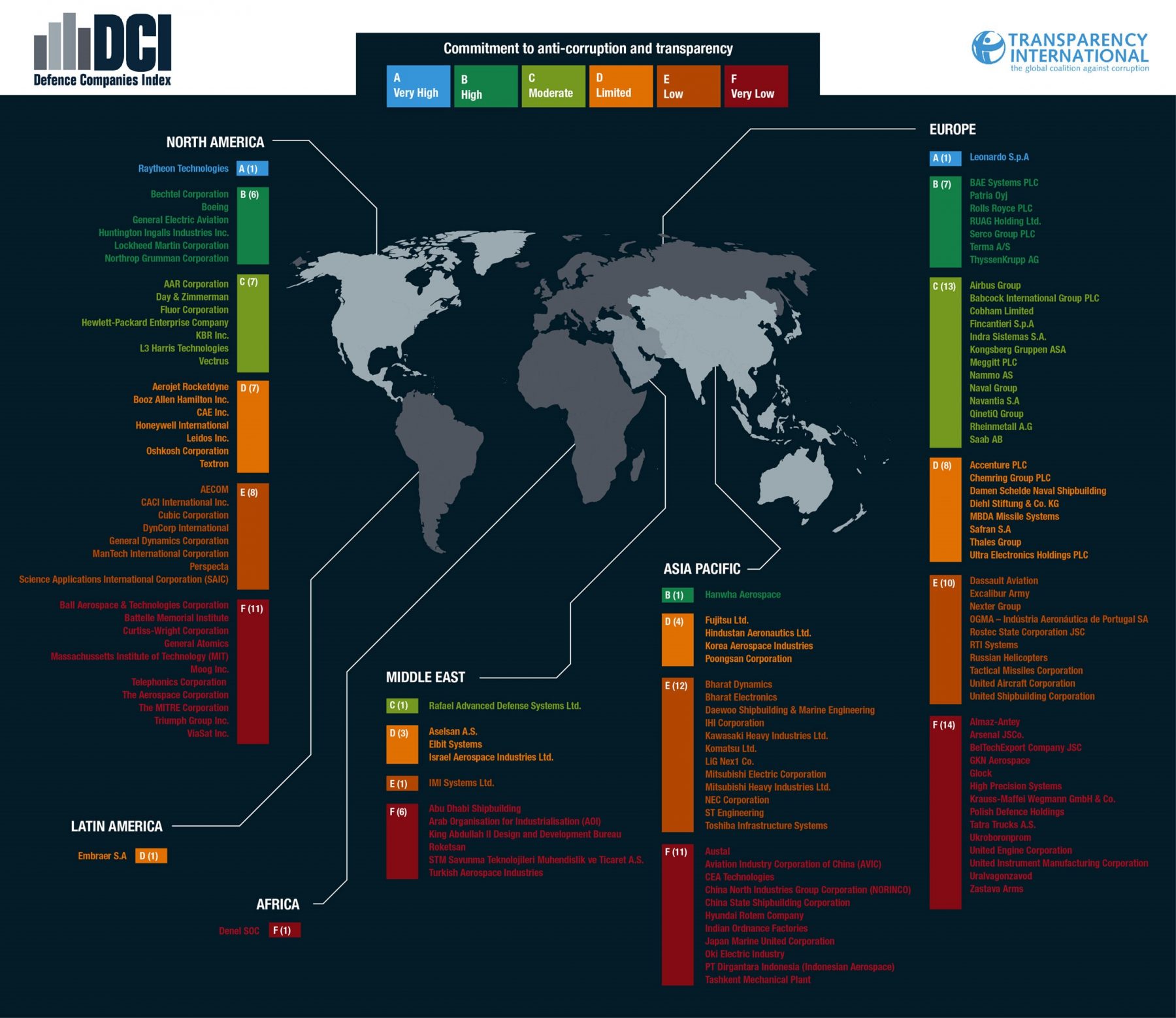
Nearly three-quarters of the world’s largest defence companies show little to no commitment to tackling corruption. That’s the headline finding from our newly published Defence Companies Index on Anti-Corruption and Corporate Transparency (DCI). It assesses 134 of the world’s leading arms companies, ranking their policies and approach to fighting corruption from A to F.
The statistic is deeply concerning, if not altogether surprising to those familiar with the defence industry. Reducing corruption in the defence sector is imperative to guarantee safety and security. Yet, a veil of secrecy, invoked ostensibly in the interests of national security, shrouds the defence sector’s activities making it especially vulnerable. The widespread use of middlemen, whose identities and activities are kept secret, further limits oversight. The impact of corruption in the arms trade is particularly pernicious. The high value of defence contracts means that huge amounts of public money may be wasted, instead of being spent on essential public services. Corruption can encourage the excessive accumulation of arms, increase the circumvention of arms controls and facilitate the diversion of arms consignments to unauthorized recipients, perpetuating conflict and costing lives and undermining democracy.
According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, of the world’s 10 largest importers of major arms between 2015-2019, eight countries – Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Algeria, Iraq and Qatar, UAE, China and India – are at high, very high or critical of corruption in the defence sector as measured by our Government Defence Integrity Index, the DCI’s sister index. Critical risk of defence sector corruption means major arms are sold to countries where they are likely to further fuel corruption, and where appropriate oversight and accountability of defence institutions is virtually non-existent.
The findings of the DCI add to this worrying picture. Nearly two thirds (61%) of the companies assessed show no clear evidence of policies or processes to assess and manage risk in markets they operate in. In addition, only 10% of the companies actively disclose full details of countries in which they and their subsidiaries operate, leaving a major gap in transparency and oversight of corporate activity.
Click here to view full screen.
The DCI has revealed that many companies score well on the quality of their internal anti-corruption measures, such as public commitments to fighting corruption and processes to prevent employees from engaging in bribery. However, because most companies publish no evidence on how these policies work in practice, it is impossible to know whether they are actually effective. Many firms do not publicly acknowledge they face increased risks when doing business in corruption-prone markets nor do they have apparent measures in place to identify and mitigate these risks. Few take measures to prevent corruption in ‘offsets’ – controversial side deals that involve a company reinvesting some of the proceeds of an arms deal into the customer’s economy but are banned in other sectors because of the corruption risks such deals pose – and most do little to counter the high-risk of bribery associated with using agents and intermediaries to broker deals on their behalf.
It is essential that companies have procedures in place to deal with these often opaque and high-risk aspects of the defence sector – including agents and intermediaries, joint ventures, offset contracting and operating in geographies considered at high risk of corruption.
We urge defence companies to increase corporate transparency through meaningful disclosures of:
- their corporate political engagement – a particularly high-risk issue in the defence sector -including their political contributions, charitable donations, lobbying and public sector appointments for all jurisdictions in which they are active;
- their procedures and the steps taken to prevent corruption in the highest risk areas, such as their supply chain, agents and intermediaries, joint ventures and offsets;
- procedures for the assessment and mitigation of corruption risks associated with operating in high-risk markets, a major risk for defence companies, as well as acknowledgement of the corruption risks associated with such practices;
- beneficial ownership and advocate for governments to adopt data standards on beneficial ownership transparency;
- all fully consolidated subsidiaries and non-fully consolidated holdings, and to state publicly that they will not work with businesses which operate with deliberately opaque structures; and
- the nature of work, their countries of operation and the countries of incorporation of their fully consolidated subsidiaries and non-fully consolidated holdings.
The DCI provides a roadmap for better practice within the defence industry. It promotes appropriate standards of anti-corruption and transparency of policies and procedures suited to the risks faced in the defence sector. Adopting these will not only reduce corporate risk, but also increase accountability and reduce the risk of corruption in the sector more widely.
The Defence Companies Index on Anti-Corruption and Corporate Transparency (DCI) seeks to assess the levels of commitment to anti-corruption and transparency in the corporate policies and procedures of 134 defence companies worldwide.
This document outlines the key methodological features of the DCI 2020, to provide further insight into the assessment process, scoring and implications of the index. The new formulation of the DCI 2020 reflects the substantial feedback received from a range of stakeholders as part of a comprehensive public consultation, which covered both the question set and the methodology itself. The DCI 2020 represents our commitment to promoting greater openness and transparency in the defence sector to help reduce corruption, build public trust, reassure investors, and build constructive relationships between companies and their employees and customers.
The Defence Companies Index on Anti-Corruption and Corporate Transparency (DCI) seeks to assess the levels of commitment to anti-corruption and transparency in the corporate policies and procedures of 134 defence companies worldwide.
We have identified 10 key areas where increased commitment to anti-corruption and transparency of information could reduce corruption risks in the defence industry. These risk areas form the
main structure of this Questionnaire and Model Answer (QMA) document.
This report examines the quality and effectiveness of defence governance across fifteen countries in Central and Eastern Europe: Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Estonia, Georgia, Hungary, Kosovo, Latvia, Lithuania, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Poland, Serbia and Ukraine. It analyses vulnerabilities to corruption risk and the strength of institutional safeguards against corruption across national defence sectors, drawing on data collected as part of Transparency International Defence & Security’s (TI-DS) Government Defence Integrity Index (GDI).
It is intended to provide governments and policymakers with an analysis of defence governance standards in the region and supply civil society with an evidence base that will facilitate their engagement with defence establishments and support advocacy for reforms that will enhance the transparency, effectiveness and accountability of these institutions.
This report details good practice guidelines and policy implications that are designed to reduce the opportunities for corruption and improve the quality of defence governance in Central and Eastern Europe. It identifies five key issues of defence governance where improvements are urgently needed in order to mitigate corruption risks: parliamentary oversight, defence procurement, transparency and access to information, whistleblowing, and military operations.
New report warns weak regulations leave door open to undue influence
October 21 – German defence policy risks being influenced by corporate interests, new research by Transparency International – Defence & Security warns.
Released today, Defence Industry Influence in Germany: Analysing Defence Industry Influence on the German Policy Agenda details how defence companies can use their access to policymakers – secured through practices such as secretive lobbying and engagements of former public officials – to exert considerable influence over security and defence decision making.
The report finds that gaps in regulations and under-enforcement of existing rules combined with an over-reliance by the German government on defence industry expertise allows this influence to remain out of the reach of effective public scrutiny. This provides industry actors with the opportunity to align public defence policy with their own private interests.
To address these shortcomings, new controls, oversight mechanisms need to be put in place and sanctions should be applied to regulate third party influence in favour of the common good and national security.
Natalie Hogg, Director of Transparency International – Defence & Security, said:
“Decisions and policy making related to defence and security are at particularly high risk of undue influence by corporate and private interests due to the high financial stakes, topic complexity and close relations between public officials and defence companies. Failing to strengthen safeguards and sanction those who flout the rules raises the risk that defence decision making and public funds are hijacked in favour of private interests.”
The report shows how lax rules around policymakers declaring conflicts of interest, and lack of adequate penalties for failing to disclose them, leaves the door open to MPs wishing to take up lucrative side-jobs. Frequent and prominent cases of job switches between the public and private defence sector compound issues of conflicts of interest and close personal relationships with inadequate oversight.
And, due to a lack of internal capacity, Germany’s defence institutions are increasingly outsourcing key competencies to industry, allowing defence companies crucial access to defence policy. The procurement of these external advisory services is not subject to appropriate oversight.
While the German constitution requires a strict control over excessive corporate influence in public sectors, too often this is not sufficiently exercised due to a lack of technical and human resources within government and parliament. In addition, insufficiently enforced legal regulations and a lack of transparency of lobbying activities enables undue influence to occur in the shadows outside of public scrutiny.
Greater transparency is necessary to ensure accountability
National security exemptions are common in the defence sector and enable institutions to override transparency obligations in favour of secrecy. However, protecting national security and ensuring the public’s right to information can both be achieved by striking the right balance where information is only classified based on a clear justification for secrecy. Transparency in defence is crucial to ensuring effective scrutiny in identifying and controlling undue influence.
“Despite the justification for secrecy in this policy area the greatest possible transparency must be created to ensure control by parliament and the public. If, in addition, human resources and expertise are lacking, advice from corporate lobbyists receive easy access,” said Peter Conze, security and defence expert at Transparency International Germany.
New lobbying register does not go far enough: we need a legislative footprint
The lack of transparency around lobbying in Germany allows industry actors to exert exceptional influence over public policy.
While Germany’s proposed new lobbying register provides a positive step towards transparency, it does not go far enough to allow effective scrutiny. External influence on legislative processes and important procurement decisions remains unaccountable without the publication of a legislative or decision-making footprint, which details the time, person and subject of a legislator’s contact with a stakeholder and documents external inputs into draft legislation or key procurement decisions.
Transparency International – Defence & Security is calling on the German government to:
- Expand the remit of the proposed lobbying register to cover the federal ministries and industry actors.
- Include requirements for a ‘legislative footprint’ that covers procurement decisions in addition to laws. The legislative footprint should outline the inputs and advice that have contributed to the drafting of laws or key policies, and substantially increase transparency in public sector lobbying.
- Introduce an effective and well-resourced permanent outsourcing review board within the Ministry of Defence to verify the necessity of external services and their appropriate oversight.
- Strengthen the defence expertise and capacity within the independent scientific service of the Bundestag, or to create a dedicated parliamentary body responsible for providing MPs with expertise and analysis on defence issues.
Notes to editors:
- The report “Analysis of the influence of the arms industry on politics in Germany” was prepared by Transparency International – Defence & Security with the support of Transparency International Germany.
- The report examined structures, processes and legal regulations designed to ensure transparency and control based on 30 expert interviews. The report is part of a comprehensive study of the influence of the defence industry on politics in several European countries.
Contact:
Harvey Gavin
harvey.gavin@transparency.org.uk
+44 (0)20 3096 7695
This report examines systemic vulnerabilities and influence pathways through which the German defence industry may exert inappropriate influence on the national defence and security agenda. Governments and industry should mitigate the risk of undue influence by strengthening the integrity of institutions and policy processes and improving the control and transparency of influence in the defence sector. Compiled by Transparency International Defence and Security with the support of Transparency International Germany, this report forms a case study as part of a broader project to analyse the influence of the arms industry on the defence and security agendas of European countries. Alongside Italy, Germany was selected as a case study due to its defence industry characteristics, industry-state relations, lobbying regulations and defence governance characteristics. The information, analysis and recommendations presented in this report are based on extensive research that has been honed during more than 30 interviews with a broad range of stakeholders and experts.
Despite promising initiatives, tackling corruption in the Nigerien security sector is still hindered by secrecy
By Flora Stevens, Project Officer – Global Advocacy
Africa’s Sahel has been plagued with conflict and insecurity for more than a decade, and the recent ramping up of violence in the region is putting already weakened armed forces under increased strain. Defence sectors across the region suffer from low levels of civilian democratic control, weak institutional oversight and are struggling to fulfil their mission to improve security in the face of a sharp uptick in attacks from non-state armed groups.
Sandwiched between jihadi militants operating in Mali and Burkina Faso to the west, Boko Haram and affiliated groups continuing to launch devastating attacks in Nigeria to the south and war-torn Libya to the north, Niger has found itself drawn into these conflicts. The complex operational requirements of bringing security to the country, with the huge distances between major settlements, porous borders and hundreds of thousands of displaced people, would pose a challenge for any armed force. But Niger, like its neighbours in the region, is also grappling with the debilitating issue of corruption in its defence sector.
Transparency International Niger has been part of the fight against corruption since 2001. The chapter works to raise public awareness of corruption issues and offers anti-corruption training to citizens. “This has enabled us to mobilise and engage citizens in the fight against corruption in our country,” said Hassane Amadou Diallo, head of the organisation. Transparency International Niger has recorded a series of major successes in its work, including a long-running advocacy campaign which culminated with Niger ratifying the United Nations Convention against Corruption in 2006, and a separate effort to abolish the ‘entrance exam’ to the civil service, a highly competitive processes which on two occasions was marred by fraud and corruption.
More recently, working with Transparency International – Defence & Security, the chapter has been involved in tackling the pernicious issue of defence corruption. Despite recent promising initiatives at national level, efforts designed to fight corruption and improve defence governance have been hindered by a high level of secrecy. It was recently revealed that almost 40% of the $312 million Niger spent on defence procurement contracts over the last three years was lost through inflated costs or materiel that was not delivered, according to a government audit of military contracts. “More than 90% of the contracts awarded to the Ministry of Defence were negotiated by direct agreement, which favoured corruptive practices and overbilling”, said Hassane Amadou. “The competition is unfair, fictitious and sometimes non-existent.” These findings came as the crisis in the Sahel continues to worsen, with hundreds of Nigerien security forces killed in fighting. At the same time, troops on the front line have complained about a lack of kit or being provided with inadequate equipment. Hassane Amadou said the audit that uncovered the extent of the procurement mismanagement would now be subject to a lengthy legal challenge. “TI Niger is hoping a fair trial will take place and that those responsible will be punished in accordance with the law,” he said.
While the findings of the audit are shocking, they unfortunately do not come as a surprise. Transparency International – Defence and Security’s Government Defence Integrity Index (GDI) recently found that while government procurement regulations are clearly spelled out in law, there is a long-standing exemption for defence procurement. The 2016 Code of Public Procurements omits goods, equipment, supplies and services related to defence and security, which effectively leaves the door open to the sort of corrupt practices uncovered by the audit.
Hassane Amadou said that TI Niger has shared the main conclusions of the GDI findings with those in charge of the defence and security forces in the country. “On the basis of the GDI, we then developed an action plan targeting various stakeholders, namely the Ministry of Defence, the parliament, defence and security officials, technical and financial partners, the media and civil society,” he said.
But while there have been signs that Niger is striving to improve its security sector governance as a key pillar for future development and long-term peace and stability, the lack of emphasis on the issue of corruption could critically undermine the effectiveness and sustainability of the whole process.
Despite the impressive reform efforts of the past few years, including the 2016-2021 Renaissance Programme, the 2016 Anti-Corruption Bill, and the 2018 National Strategy to Fight Corruption, Niger is struggling to ensure their effective implementation. The Nigerien government should primarily focus on closing this gap and on rectifying loopholes that allow for corruption in the defence procurement sector to thrive. This could include revising relevant legislation to ensure it effectively applies to all defence acquisitions, with no exceptions.
It is fundamental for the Nigerien military to fully grasp the intrinsic link between corruption and operational efficiency. An important focus area must be the deployment of trained professionals to monitor corruption risks in the field. There is unfortunately currently little evidence of this. There is no pre-deployment corruption-specific training for personnel and no guidelines on addressing corruption risks during operations.
To tackle the security threats Niger is facing, mitigating corruption risks in the defence sector is paramount and requires a robust, disciplined and integrated approach on the part of the Niger government. It needs to ensure civilian oversight is strengthened through well-functioning oversight mechanisms, while making sure corruption is approached in a systemic or comprehensive manner during troop deployment.
By Matthew Steadman, Project Officer – Conflict & Insecurity
2019 was a deeply concerning year for the Sahel. Attacks by extremist groups have increased five-fold in Mali, Niger and Burkina Faso since 2016, with the UN now describing the violence as “unprecedented”. The past year was the deadliest by far with more than 4,000 deaths reported. Niger lost 89 soldiers in a single attack by Islamic State in Changodar in January, whilst two ISGS attacks in Mali in November claimed the lives of 92 soldiers. In Burkina Faso alone, 1,800 people were killed in the past year due to extremist violence. The intensification of extremist activity in the Sahel threatens to engulf West African coastal states, as already weakened national defence and security forces come under increasing pressure. Much international coverage of the developing events has focussed on the operational aspect of the crisis, from the various armed groups operating in the region to the international response, spearheaded by France’s Operation BARKHANE but also including MINUSMA, the G5 Sahel, the United States and the EU. However, one aspect that has been regularly overlooked is the poor capacity of the region’s national defence forces to respond to security threats as a result of poor defence governance, corruption and weak institutions.
Corruption and conflict go hand in hand, with corruption often fuelling violence and subsequently flourishing in afflicted regions. Because of corruption and poor governance, defence and security actors are often seen not as legitimate providers of security, but as net contributors to the dynamics of conflict; with poor training, management and institutional support leading to a downward cycle in which it is the civilians that more than often feel the brunt – as has been seen in Burkina Faso, Nigeria and Mali. When security institutions are perceived as corrupt, public confidence in government erodes further. Fragile governments that are unable to respond to the needs of citizens can exacerbate existing grievances, heightening social tensions and hastening the onset of violence. Across the Sahel, armed groups have been able to entrench themselves first and foremost in those areas which have been neglected by weakened and corrupt central authorities, often by positioning themselves as providers of security, justice and basic services. In this way, it is crucial to view corruption not just as the consequence of conflict, but more often as its root cause and therefore a critical element for any attempt at resolution to address.
Against this backdrop, research by Transparency International – Defence & Security’s Government Defence Integrity Index (GDI), highlights the deficiencies in the safeguards which should provide protection against corruption in the defence sectors of Burkina Faso, Cote d’Ivoire, Ghana, Mali, Niger and Nigeria, increasing the likelihood of defence funds and capabilities being wasted due to mismanagement of human, material and financial resources. In doing so, the GDI outlines a number of key issues which need to be addressed in order to enhance security forces’ ability to respond to threats and protect local communities:
Reinforce parliamentary oversight
Despite most countries having formal independent oversight mechanisms for defence activities, policies and procurement, our research has found that these are often only partially implemented, easily circumvented and insufficiently resourced to carry out their mandates. The result, is defence sectors which are still largely the preserve of the ruling elite and shrouded in secrecy, raising concerns over the use of vital defence funds and the management of resources and assets.
Strengthen anti-corruption measures in personnel management and military operations
Personnel management systems are also vulnerable, with inadequate or non-existent whistleblowing protections and reporting mechanisms, unclear appointment, and promotion systems open to nepotism, and codes of conduct which fail to specifically mention corruption or enforce appropriate sanctions. Equally, despite many countries in the region being actively engaged in on-going counter insurgencies, there is no evidence of Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso or Nigeria having up to date doctrine which recognises corruption as a strategic threat to operations, meaning there is little if any appropriate training on the pitfalls associated with operating in corrupt environments and little appreciation of how soldiers’ conduct might exacerbate the violence they are trying to quell.
Increase transparency and external oversight of procurement processes
Perhaps most concerning of all is that corruption risks in defence procurement remain extremely high across the region. The procurement process is opaque and largely exempt from the checks and balances which regulate other areas of public procurement in countries like Mali and Niger for instance. Across the region, the effectiveness of audit and control mechanisms over the acquisition of military goods and services is heavily restricted by blanket secrecy clauses and over-classification of defence expenditure. This raises serious concerns over the utility, relevance and value for money of purchased equipment and increases the risk of that frontline troops will not have the resources required to deliver security.
Despite these structural vulnerabilities, international assistance in the region has been heavily focussed on security assistance rather than on improving the underlying structures that govern and manage defence and security in the states that make up the region. The 13th January summit between French President Emmanuel Macron and the leaders of the G5 Sahel countries, was emblematic of this with the meeting focussed on reaffirming France’s military presence in the region and announcing the deployment of further troops, whilst side-lining the governance deficit which underlies so much of the crisis. Programmes have tended to focus on training and equipping military and police forces in Mali and Burkina Faso for instance, or improving strike capabilities by investing in US drone bases in Niger. The concern however, is that the impact of these efforts will be blunted without a more sustained engagement in addressing the more fundamental failings that lay at the hearty of the problem. Mali’s recent announcement of a recruitment drive for 10,000 new defence and security forces personnel for example, will only be effective if it is accompanied with improvements in the way these troops are trained, led, equipped and managed and if the political and financial processes which govern them are strengthened and corruption risks reduced.
A successful response, at the national, regional and international levels, to the violence cannot be just security focussed. Poor defence governance and corruption risks will continue to hamper national forces’ operations and will hinder the impact of international efforts which support them. A more comprehensive approach is needed which addresses the underlying corruption risks which permeate the region’s defence sectors. Improving oversight, transparency and accountability is a critical step in securing a sustainable peace in the region and ensuring that defence and security apparatuses do what they should, which is to further the human security of populations that they should be serving.
January 14, 2020 – Sweeping reforms to controls on American arms sales abroad are increasing holes in checks to identify and curb corruption – measures that can also be used to assess whether sales may help or hurt efforts to address terrorist threats and attacks – according to new research by Transparency International Defense & Security.
Launched today, Holes in the Net assesses the current state of US arms export controls by examining corruption risk in three of the most prominent sales programs, which together authorized at least $125 billion in arms sales worldwide for fiscal year 2018.
Across all three different arms sales programs, which are managed by the Defense, State, and Commerce Departments, there is a clear gap in American efforts to assess critical, known corruption risk factors. This include the risks of corrupt practices – such as theft of defense resources, bribery, and promoting military leaders based on loyalty instead of merit – weakening partner military forces.
The United States is one of the biggest arms exporters to countries identified as facing ‘critical’ corruption risk in their defense sector, including Egypt, Jordan, Oman, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia, according to recent analysis by Transparency International – Defense & Security.
Steve Francis OBE, Director of Transparency International – Defense & Security, said:
“Given the corrosive effect corruption has on military effectiveness and legitimacy, it is deeply concerning to see that these reforms to American arms export controls have made it easier for practices like bribery and embezzlement to thrive. In order to ensure American arms sales do not fuel corruption in countries like Egypt, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia, it is imperative to understand and mitigate the corruption risks associated with countries receiving US-made weapons before approving major arms deals.”
Of the three programs assessed in the report – Foreign Military Sale, Direct Commercial Sale, and the 600 Series – the 600 Series was identified as having the biggest gaps in its anti-corruption measures. Overseen by the Commerce Department, sales through this program do not require declarations on a series of major corruption risk areas, including on certain arms agents or brokers, political contributions, company subsidiaries and affiliates, and any defense offsets. These areas are common conduits used for bribery and political patronage.
More recently, the Trump administration has proposed moving many types of semi-automatic firearms and sniper rifles to Commerce Department oversight. The proposal calls for additional controls for firearms, but also reduces overall oversight of small and light weapons exports.
Colby Goodman, Transparency International – Defense & Security consultant and author of the report, said:
“Over the past 30 years, America has established some of the strongest laws to prevent bribery and fraud by defense companies engaged in arms sales. However, defense companies selling arms through the 600 Series program no longer have to comply with key anti-corruption requirements. As a result, US officials will likely find it harder to identify and curb bribery and fraud in sales of arms overseen by the Commerce Department.”
The report analyzed five priority corruption risk factors for American arms sales programs: 1) Ill-defined and unlikely military justification; 2) Undisclosed or unfair promotions and salaries in recipient countries; 3) Under-scrutinized and illegitimate agents, brokers and consultants; 4) Ill-monitored and under-publicized defense offset contracts, and 5) Undisclosed, mismatched or secretive payments.
The report makes a series of policy recommendations that would help strengthen anti-corruption measures in these prominent arms sale programs, including:
- Creating a corruption risk framework for assessing arms sales through programs managed by the Defense, State, and Commerce Departments. These assessment frameworks must examine key risk factors identified in our report, including theft of defense resources and promoting military leaders based on loyalty instead of merits, among others.
- Strengthening defense company declarations and compliance systems for sales of arms overseen by the Commerce Department, including declarations of any defense company political contributions, marketing fees, commissions, defense offsets, and financiers and insurance brokers of arms – all clear conduits for corruption.
- Increasing transparency on arms sales and actions to combat arms trafficking overseen by the Defense, State, and Commerce Department. Critically, the Defense and State Departments need more details on defense offsets in order to properly review proposed arms sales. There is virtually no information on Commerce Department approved arms sales.
- Legislation requiring for firearms and associated munitions to remain categorized as munitions to ensure further relaxing of export controls do not adversely impact US national security or foreign policy objectives.
Notes to editors:
Interviews are available with the report author.
Holes in the Net is available to download here.
Saudi Arabia, a major importer of US-made arms, failed to defend against an attack on its oil facilities in September 2019. Reports have suggested that corrupt ‘coup-proofing’ measures designed to shield the ruling family likely contributed to the ineffective response.
Contact:
Harvey Gavin
harvey.gavin@transparency.org.uk
+44 (0)20 3096 7695
+44 (0)79 6456 0340
Corruption is widely recognized as one the major stumbling blocks in US government efforts to improve the capacity of foreign defense forces to address shared international security threats over the past 15 years.
This report assesses the current state of US arms export controls to identify and curb corruption in US arms sales. It first highlights critical corruption risk factors the United States should consider in order to help prevent corruption and fraud in its arms sales. The report then assesses US laws, policies, and regulations aimed at identifying and mitigating corruption and fraud risks in US arms sales.
By Steve Francis OBE, Director of Transparency International – Defence & Security
The Government Defence Integrity Index (GDI) is the first global analysis of corruption risks and the existence and enforcement of controls to manage that vulnerability in defence and security institutions, highlighting priority areas for improvement. Key to analysing results from the Index is understanding that the GDI measures corruption risk, not levels of corruption per se.
GDI data will be released in regional waves through 2020. Results from the most recent wave – the Middle East and North Africa – were published in November.
On the whole, the data paints a fairly bleak picture for the region. Tunisia leads the group with an overall grade of “D,” indicating a “high” degree of defence corruption risk, while the other 11 assessed countries received either an “E” or an “F” – signalling “very high” or “critical” levels of risk. Regional averages reflect a similar performance across the individual risk areas – political, financial, personnel, operations, and procurement.
With these findings in mind, what can the analysis of the GDI’s result teach us about protracted cases of armed conflict, political instability, and insecurity that seem to characterise the region?
1. In many cases, high defence corruption risk is symptomatic of wider governance issues.
The GDI’s political risk indicators and aggregated scores on anti-corruption themes examine broader issues of legislative oversight, public debate, access to budgetary information, and civil society activity – issues that don’t just impact the defence sector. Indeed, this area of the assessment highlights essential ingredients for any open and transparent government that engages constructively with its citizens. As most of the assessed MENA countries are governed by authoritarian regimes, we should not be too surprised then that these wider governance challenges also exist in the defence sector. Specifically, our data found a clear lack of external oversight, audit mechanisms, and scrutiny of defence institutions across the region.
Table: MENA region average scores for key political risk indicators and anti-corruption themes
| Question | Indicator/Theme | Score | Grade |
| Q1 | Legislative scrutiny of defence laws and policies | 15 | F |
| Q3 | Defence policy debate | 9 | F |
| Q4 | CSO engagement with defence and security institutions | 15 | F |
| Q6 | Public debate of defence issues | 23 | E |
| Q13 | Defence budget scrutiny | 10 | F |
| Q17 | External Audit | 8 | F |
| Aggregate | Openness to civilian oversight | 14 | F |
| Aggregate | Oversight | 14 | F |
| Aggregate | Budgets | 15 | F |
| Aggregate | Transparency | 15 | F |
| Aggregate | Undue influence | 19 | E |
2. Countries with the highest defence corruption risk are also significant arms importers.
Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Algeria were three of the world’s top five arms importers from 2014-2018. All three received an “F” grade in the GDI, with Egypt and Algeria receiving the bottom two regional scores (6/100 and 8/100, respectively).
The region has gaps in export controls, with only Lebanon and Palestine having ratified the Arms Trade Treaty, in addition to related risks like a lack of regulation around lobbying in defence and virtually no transparency around defence spending.
Although major arms exporters to the region like the United States have rules against the transfer of arms to third parties, end-use monitoring is not always consistent or comprehensive. This is especially troubling given that top arms importers in the region are either directly involved in or are arming parties to the devastating conflicts in both Yemen and Libya.
3. Low-scoring countries also exhibit high corruption risk by blurring the line between business and defence.
While the region as a whole scored poorly on indicators relating to the beneficial ownership (47/100) and scrutiny of military-owned businesses (44/100), these risks are greatest in countries with extensive military-run industries and/or significant natural resources. In Egypt for example, the military owns lucrative businesses across industries ranging from food and agriculture to mining, but has few controls in place for regulating these ventures. In Algeria, a largely state-owned economy renowned for high levels of corruption and patronage, there are a range of potential implications now that the military has stepped in to fill the vacuum following the ousting of President Bouteflika in March 2019 following mass public unrest.
The Gulf monarchies offer an example of how defence and business can overlap at the level of the individual. In the assessment for Saudi Arabia, we found that members of the royal family who serve in senior military positions also have controlling or financial interests in businesses related to the country’s petroleum sector. In the UAE as well, our research found that Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi and Deputy Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces, is also the Chairman of a company dealing in natural resources.
On the other end of the spectrum, the GDI found that in Morocco, Palestine, and Tunisia, defence and security institutions do not own businesses of any significant scale, thereby removing a significant source of corruption risk.
As the GDI data shows, the risk of defence corruption in the MENA region is a serious concern with the potential to exacerbate ongoing conflict and instability. However, robust tools like the GDI can help governments to identify gaps in safeguarding practices – the first step in a process towards reform – while supporting civil society and oversight actors in countries across the region in conducting evidence-based advocacy.
Last week, Transparency International Defence & Security (TI-DS) attended the Fifth Annual Conference of States Parties (CSP5) to The Arms Trade Treaty (ATT), where delegations of the 104 signatories gathered to review the status of the Treaty and set the agenda for the year ahead.
Five years since the introduction of the Arms Trade Treaty, there are plenty of reasons for gloom. This year’s Conference focused on two topics in particular: diversion and gender-based violence. Despite being covered under the ATT – articles 7 and 11 respectively – states have been struggling to address these illicit arms flows and reduce gender-based violence. Any advances made by new states ratifying the treaty – most recently Canada and Botswana – have been countered by the lack of representation from some of the world’s largest arms exporters such as Russia, China and now the US, which withdrew its signature from the treaty.
Meanwhile transfers of weapons continue to increase, and implementation challenges are becoming obvious. However, at this point the question is not one of giving up, but rather one of what can we do to make the Treaty more effective?
The CSP is open to civil society, encouraging participation in side events and lively debates. Only one panel discussion was restricted to state signatories – out of 20 in total. While this shows the role and importance of civil society participation in the ATT process, more can be done to foster this cooperation during the rest of the year.
TI-DS has an important contribution to make to this movement. By working together with Transparency International’s national chapters and other local partners we can do more to support national adoption and implementation strategies.
What does that mean in practice? Here are five learnings from the CSP5 that point the way:
1. Provide the evidence-base for arms control decisions
When deciding whether to approve an arms export application, state licensing bodies must consider a wide range of factors about the importing country – from the internal security situation to regional stability and risk of diversion from the stated end-user. Most states will assess these factors through an in-depth risk assessment of the viability of the export, using both classified and open source information.
Research reports and studies conducted by civil society can provide valuable sources of information for states. TI’s Government Defence Anti-Corruption Index (GI) provides an analysis of the corruption risks within the defence establishments of 90 countries worldwide. Government export control agencies can use this data to consider the risk of corruption in importing countries to inform the likelihood of diversion or misuse of weapons.
2. Raise awareness of the ATT and its relevance to national governments
As organisations with a particular national, regional or thematic focus, civil society organisations (CSO) are well-placed to provide expert insight into the arms control issues facing a country. In states that have not yet adopted the ATT – or are working towards ratifying it – CSOs can work with government agencies, industry and think tanks to facilitate a national debate on the importance and benefits of compliance with the treaty. They can build coalitions of interested parties to work towards a common goal, as shown by the continued contribution made by the Control Arms Coalition.
Moreover, civil society – unlike governments, industry or think tanks – often have the grassroots networks and community buy-in needed to build pressure and hold states to account for their promises when it comes to international obligations such as the ATT.
3. Assist parliaments and governments in implementing the treaty
CSOs working on arms control issues are in general able to develop a broader knowledge base than parliamentarians and other actors whose day jobs only touch upon this complex topic. The potential for cooperation between the two was illustrated by an example presented at this year’s conference which highlighted the role of the Small Arms Survey NGO, who assisted Japan by conducting a gap analysis of its ATT implementation progress.
From giving evidence to a parliamentary committee to providing MPs with research to inform parliamentary questions, CSOs can work directly with concerned parliamentarians to maintain the political will and internal pressure needed to support proper implementation of the treaty.
4. Monitor ATT progress and violations
As third-party stakeholders, CSOs are often able to raise and address controversial topics.
CSOs working in-country may encounter evidence of a violation of treaty obligations and report it to the government. Many CSOs also have the ability and expertise to synthesise these cases into national and regional trends, thereby providing governments with a tool to develop mitigation strategies and improve their progress in implementing the ATT.
By providing a solid evidence base with clear policy recommendations, CSOs can help states reflect on the progress they have made and highlight areas that need strengthening.
5. Achieve universalisation through improved reporting and transparency
The substantial differences in the way that states submit their ATT reporting obligations constitute a barrier to universalisation. Although 83 per cent of states used the reporting template, some are still submitted incomplete or in non-readable format or indeed in a completely different format that is difficult to consolidate. On top of this, 25 per cent of states failed to submit an annual report at all.
CSOs can work with national governments and industry to promote transparency and common reporting standards, which in turn allows for comparability and more effective implementation of treaty obligations.
The future of the ATT may be uncertain, but states can’t do it alone and nor should they. Civil society can help national governments bridge the gap between policy and practice by providing hands-on insight and analysis into arms control issues worldwide.